Holland Hospital News and Stories
Holland Hospital managed websites use cookies to enhance your website experience. By navigating our websites, you agree to the Website Terms of Use. For more information, please review our Website Privacy Policy.
Displaying 1 - 10 of 519
Image
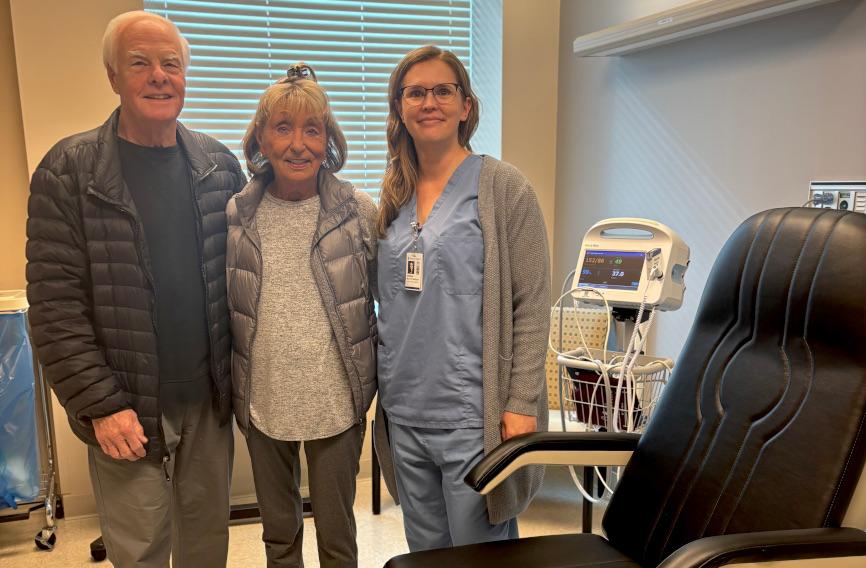
A Lifetime of Care Comes Full Circle: Gary and Linda’s Story
Donor Stories
Patient Stories
For Gary and Linda Speet, Holland Hospital isn’t just part of their community, it’s part of their lives, their history, and even their family legacy.
Image
Holland Hospital Celebrates National Blood Donor Month, Honoring Local Heroes Who Saved Over 500 Lives
Media Releases
News
In recognition of National Blood Donor Month throughout January, Holland Hospital is celebrating the extraordinary generosity of our community members who donated blood in 2025.
Image

Holland Hospital Orthopedic Surgeon Reaches Milestone with 2,000 Robotic-Assisted Knee Replacements
Media Releases
News
Holland Hospital’s Bone & Joint Center is proud to announce that orthopedic surgeon Derick Johnson, DO has successfully performed 2,000 robotic-assisted knee replacements using the Mako™ Knee system from Stryker Corporation, positively impacting thousands of people across West Michigan.
Image

Holland Hospital Shares 2025’s Most Popular Baby Names
Media Releases
News
Every name tells a story, and at Holland Hospital’s Boven Birth Center, more than 1,200 stories began in 2025. Holland Hospital is excited to share the names that captured the hearts of parents at Boven Birth Center this year.
Image
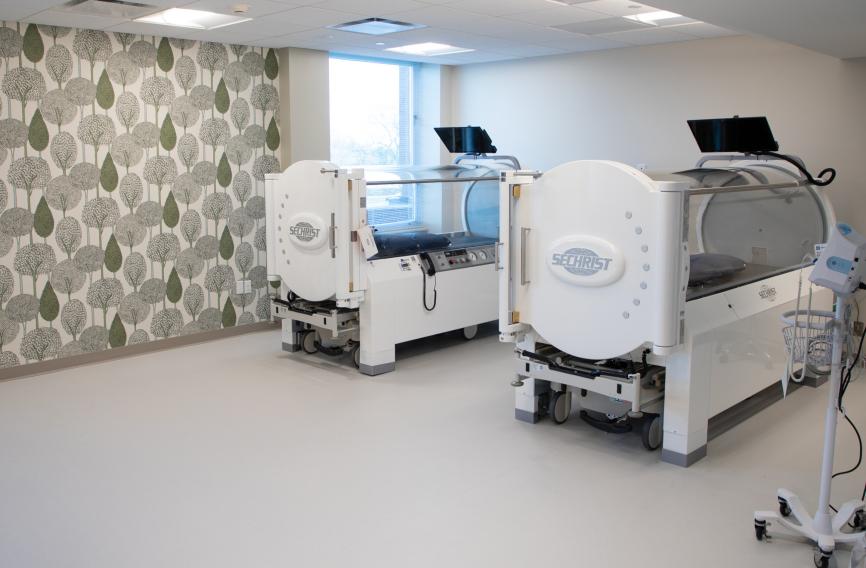
Holland Hospital Announces Expanded Services in New Wound Healing & Hyperbaric Medicine
Media Releases
News
Holland Hospital is proud to announce the expansion and enhancement of its comprehensive Wound Healing & Hyperbaric Medicine Program, offering West Michigan patients access to advanced, hospital-based treatment for chronic and complex wounds.
Image
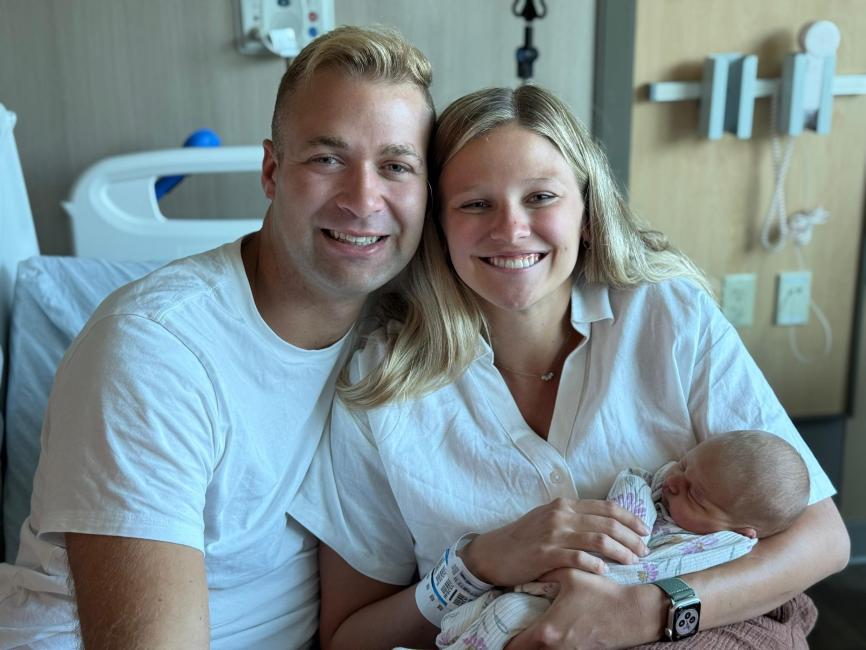

Tate’s Journey: From Birth to Breastfeeding Confidence
Patient Stories
From a calm birth to overcoming breastfeeding hurdles, Tate Bonnema discovered the power of support and community at Holland Hospital, finding confidence and connection every step of the way.
Image
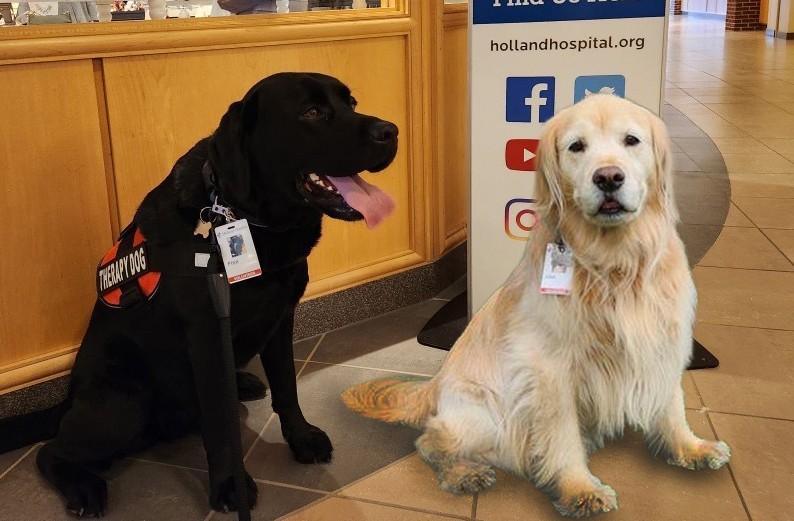

Holland Hospital Expresses Paws-itive Gratitude for Dedicated Volunteers This Holiday Season
Media Releases
Pet therapy volunteer Carin Arvidson and her dogs are spreading joy and unconditional love to patients.
Image

Holland Hospital Shares Health and Safety Tips for a Healthier and Happier Thanksgiving Holiday
Media Releases
In the season of gratitude with Thanksgiving quickly approaching, Holland Hospital aims to help keep West Michigan residents healthy this holiday season.
Image

Holland Hospital Earns Healthgrades Specialty Care Excellence Award for Third Consecutive Year, Among Nation’s Top 10%
Media Releases
News
Holland Hospital is the only hospital in Michigan to receive the Outpatient Joint Replacement Excellence Award and the Outpatient Orthopedic Surgery Excellence Award in 2026.
Pagination
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- …
- ›› Next page
- Last » Last page
